Manage Data Queries with BigQuery and Runme
Runme simplifies the management and execution of tasks while documenting your process. With Runme, you can integrate with BigQuery to run queries easily and efficiently.
In this guide, you will learn how to manage data queries using BigQueris and Runme.
Prerequisites
To follow up on this guide, ensure you have the following:
- Install Runme Extension and Make it Your Default Markdown Viewer
Install the Runme extension in your VS Code editor. Runme also provides other client interfaces where you can run your Markdown file. Once installed, make Runme your default Markdown viewer.
- Google Cloud SDK
Install Google Cloud SDK to interact with Google Cloud resources. To install it, run the command below.
brew install --cask google-cloud-sdk
If you are using any other platform, see the GCP's official docs to learn how to install Google Cloud SDK for your specific platform.
Authenticate with Google Cloud
The first step to take is to authenticate your Google Cloud account using the gcloud auth feature, which allows you to have access to Google Cloud resources. To do this, run the command below:
gcloud auth login
Once this command is executed, a browser window will open where you can log in with your Google account. After logging in, you can explore the Gcloud components.
- List Available Components
To list all available or installed components of your Google Cloud SDK, run the command below.
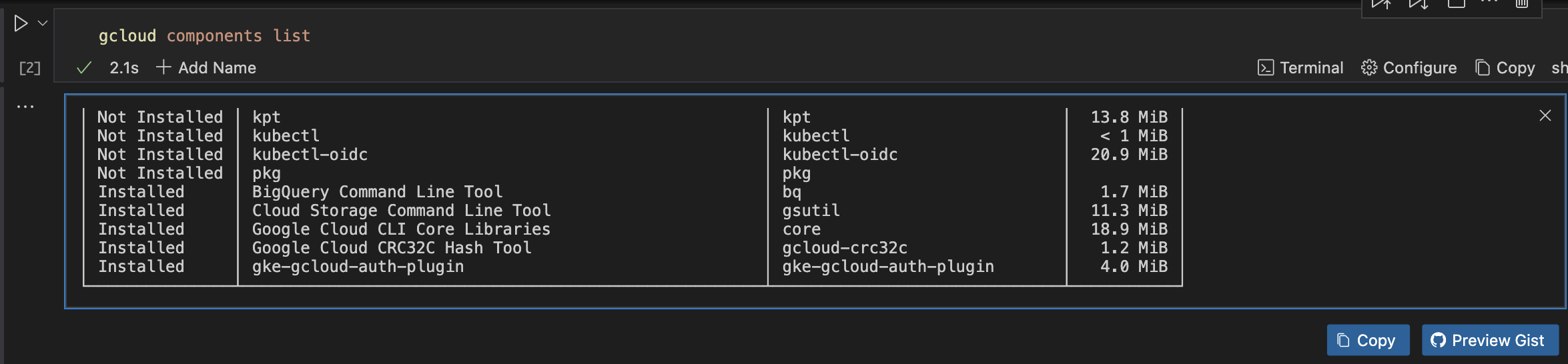
gcloud components list
When the command is executed successfully, you will see a list of all available components, similar to the image below.
- Update Google Cloud Components
After getting a list of all available and installed components, you may want to update them. To do that, run the command below.
gcloud components update
- Install the BigQuery Component
With the authentication completed, you can proceed to install your BigQuery component. Run the command below to do that.
gcloud components install bq
Set Up Your Project
Now, you have successfully completed the authentication phase. The next step is to set up your project.
To do that, you first need to set up your Google Cloud project ID using the Runme Environment Variable Prompt. This allows you to specify the project you want to work on within your notebook. To set your project ID, run the command below:
export PROJECT_ID="runme-ci"
echo "PROJECT_ID set to $PROJECT_ID"
Replace
runme-ciwith the ID of your project.
Next, Configure the gcloud CLI to use your specific Google Cloud project. Run the command below to do that.
gcloud config set project $PROJECT_ID
BigQuery Operations
In this section, we will explore various BigQuery operations.
- Query a Dataset With Runme
With Runme features, you can successfully run and display your query's output, formatting it into a table for easy navigation.
To do this, you first need to set your FORMAT. Using Runme’s environment variable, you will be prompted to set the FORMAT. Run the command below in your code cell.
export FORMAT="json"
echo "FORMAT set to ${FORMAT}"
The next step is to execute your query.
To do this, set the code cell programming language to SQL and also give your code cell a name. For this example, we will call our code cell QUERY. Run the command below.
SELECT title, num_characters, timestamp, id, revision_id FROM
`bigquery-public-data.samples.wikipedia`
WHERE num_characters < 67100
LIMIT 10;
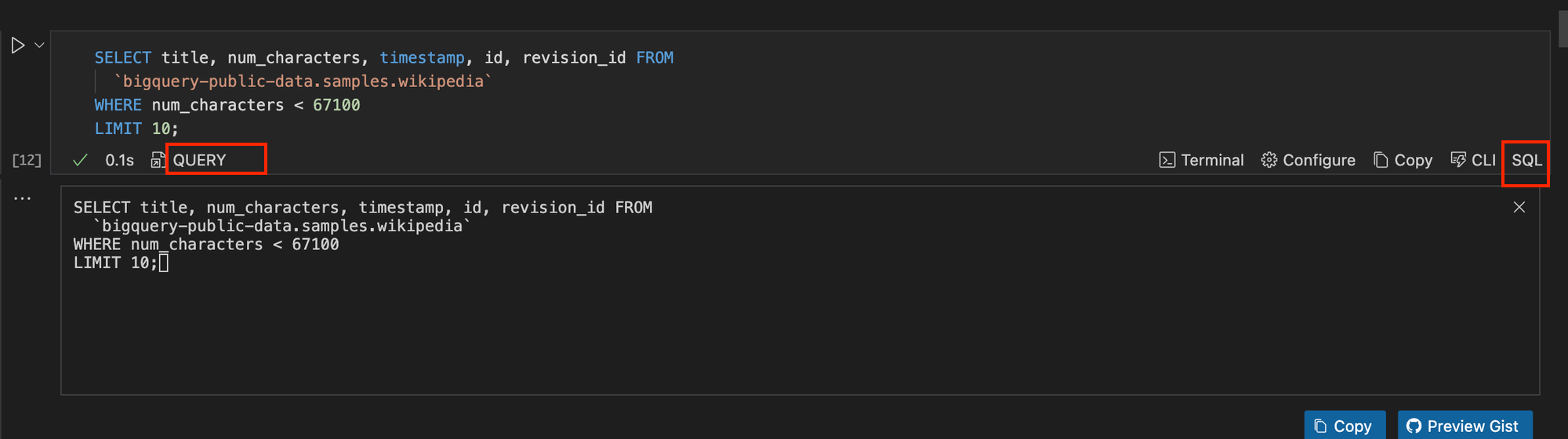
Next, run the command below while disabling the interactive mode of the code cell.
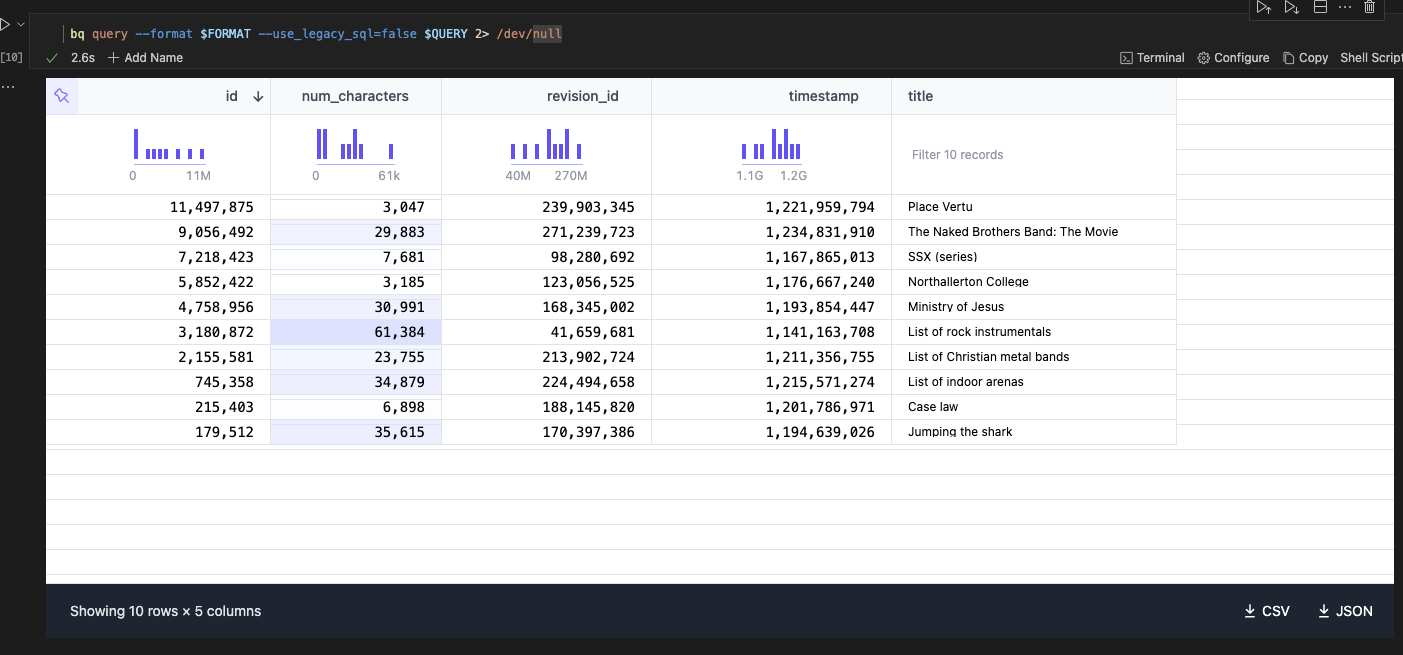
bq query --format $FORMAT --use_legacy_sql=false $QUERY 2> /dev/null
When this is successful, you will get an output similar to this. You can change the presentation of your data. To do this, click the menu icon (three vertical dots) beside your output. A small dashboard will pop up. Click on Change Presentation to change how the data is presented. You will be prompted to select how you want to view your data.
- Querying BigQuery Dataset
You run a query against your BigQuery dataset. For example, to select data from a specific table, use the following command:
bq query --use_legacy_sql=false 'SELECT * FROM `[PROJECT_ID].[DATASET].[TABLE]` LIMIT 10'
Ensure that you replace all PROJECT_ID, DATASET, and TABLE with the information specific to you, just like the code block below. Now, run the command.
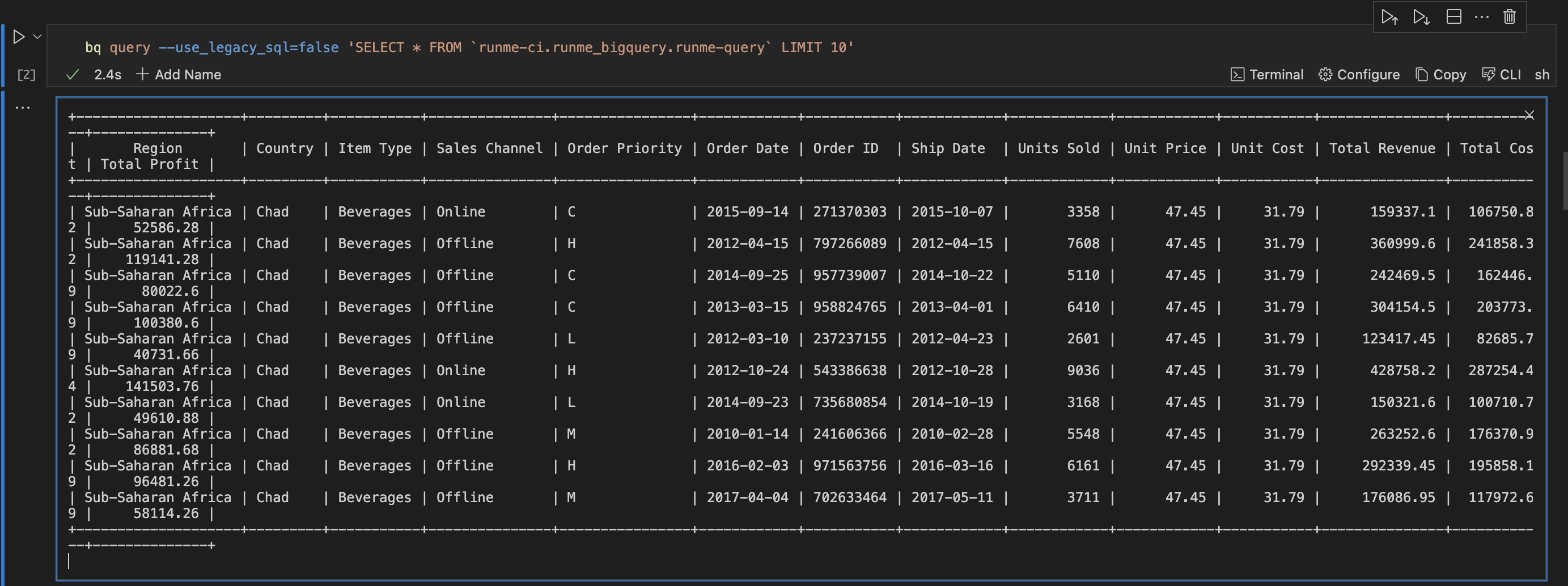
bq query --use_legacy_sql=false 'SELECT * FROM `runme-ci.runme_bigquery.runme-query` LIMIT 10'
This command will return the first 10 rows from the runme-query table in the runme_bigquery dataset. Here is the output.
- Listing Datasets and Tables
The next Bigquery operation we will explore is how to list datasets and tables.
To get a detailed list of all datasets in your project, run the command below:
bq ls
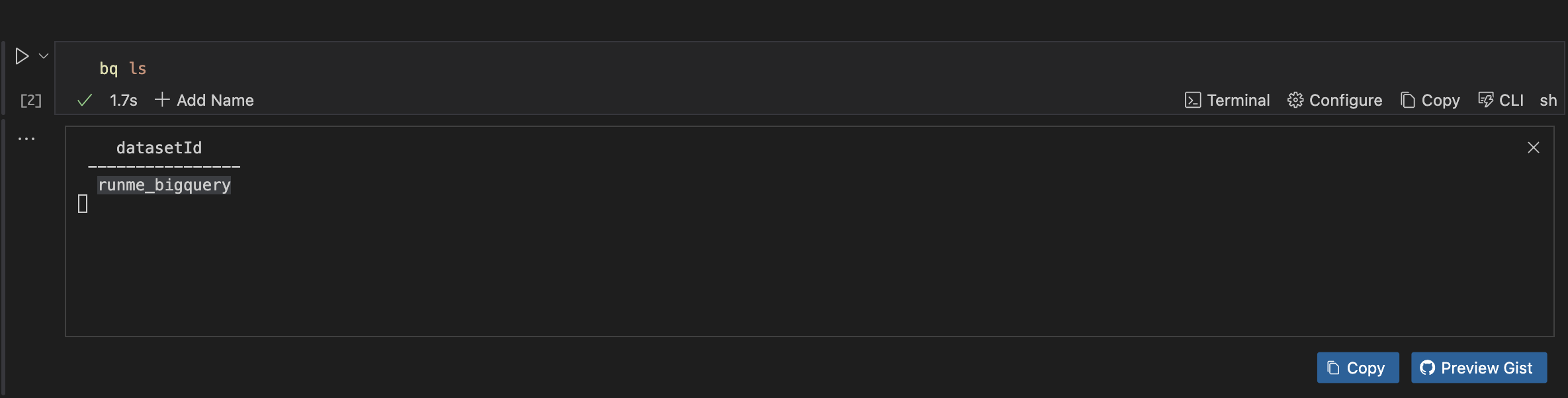
Additionally, you can list all tables in a specific dataset (e.g., runme_bigquery). To do this, run the command below.
bq ls runme_bigquery
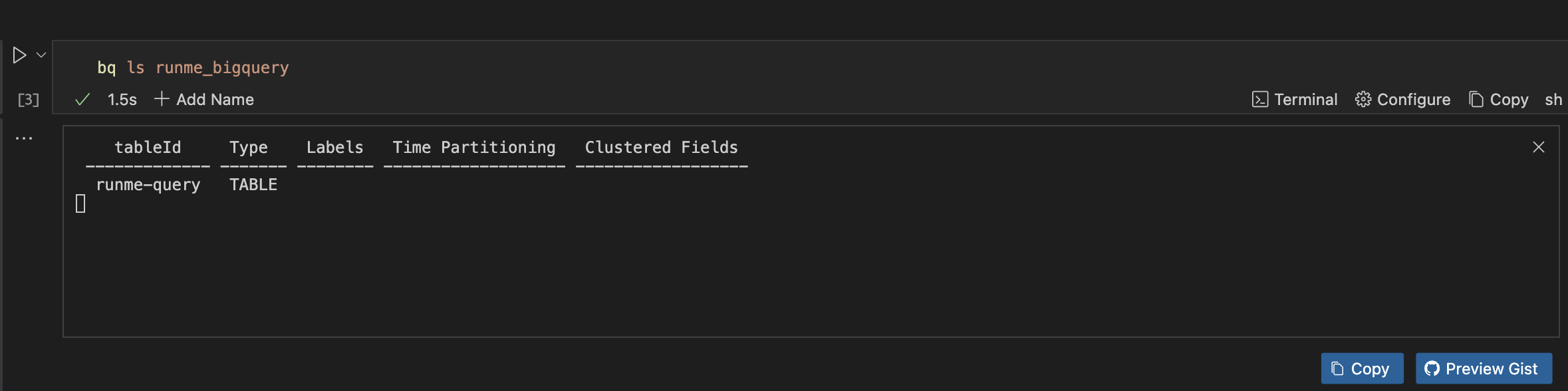
To show details of a specific table (e.g., runme-query), run the command below.
bq show runme_bigquery.runme-query
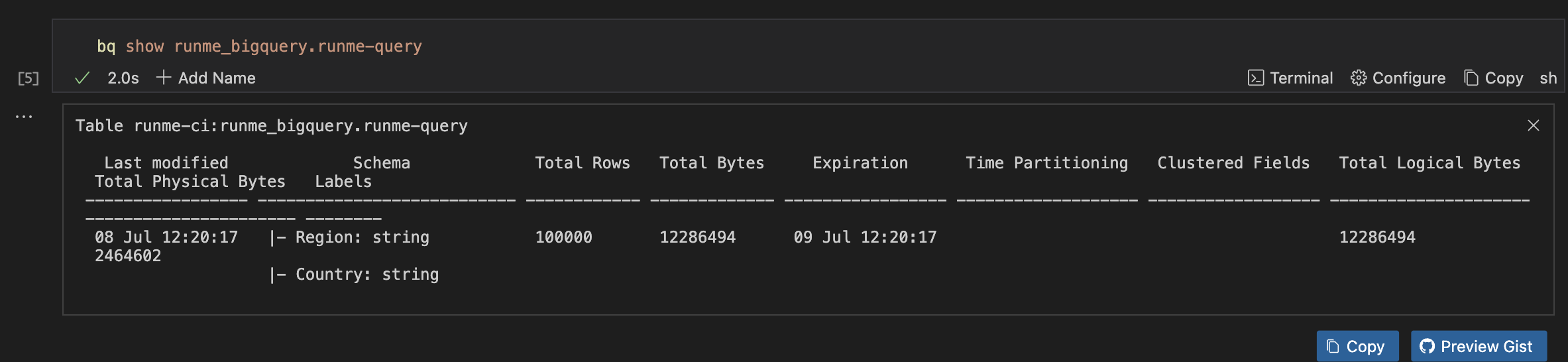
Be sure to change the runme-query with your project dataset.
- Load Data into a Table
You can also load data from a CSV file into a table in Google BigQuery. To do that, run the command below:
bq load --source_format=CSV [DATASET].[TABLE] [PATH_TO_CSV_FILE] [SCHEMA]
Ensure that you provide the information for the DATASET, PATH_TO_CSV_FILE and SCHEMA like the code block below. Now, run the command.
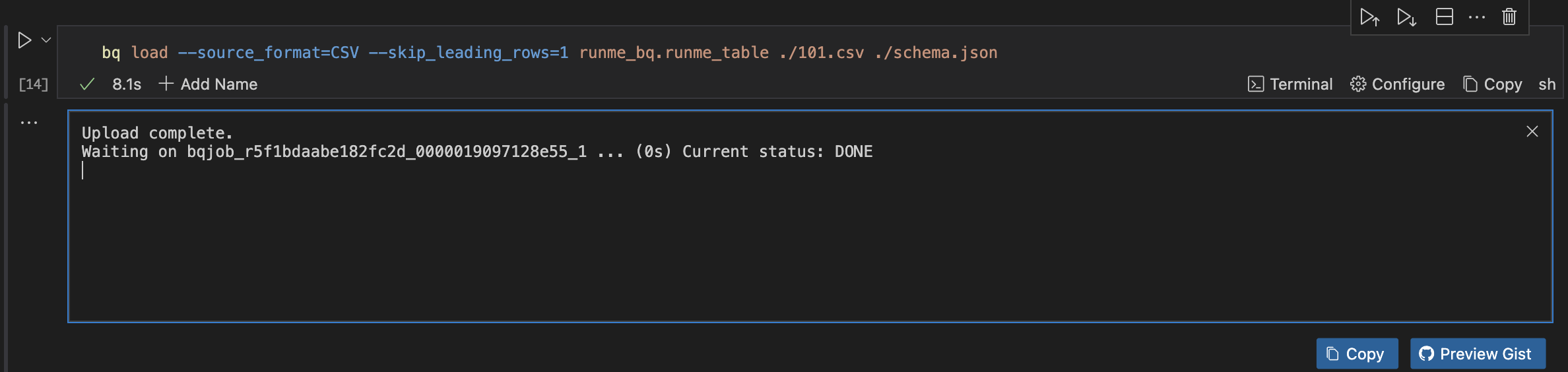
bq load --source_format=CSV --skip_leading_rows=1 runme_bq.runme_table ./101.csv ./schema.json
Once that is done, you will get an output similar to this.
- Export Data from a Table
Extracting data from a table and saving it as a CSV file in your storage system(GCS bucket) is equally possible. To do that, run the command below
bq extract --destination_format=CSV [DATASET].[TABLE] gs://[BUCKET]/[FILE_NAME].csv
- Creating a Dataset
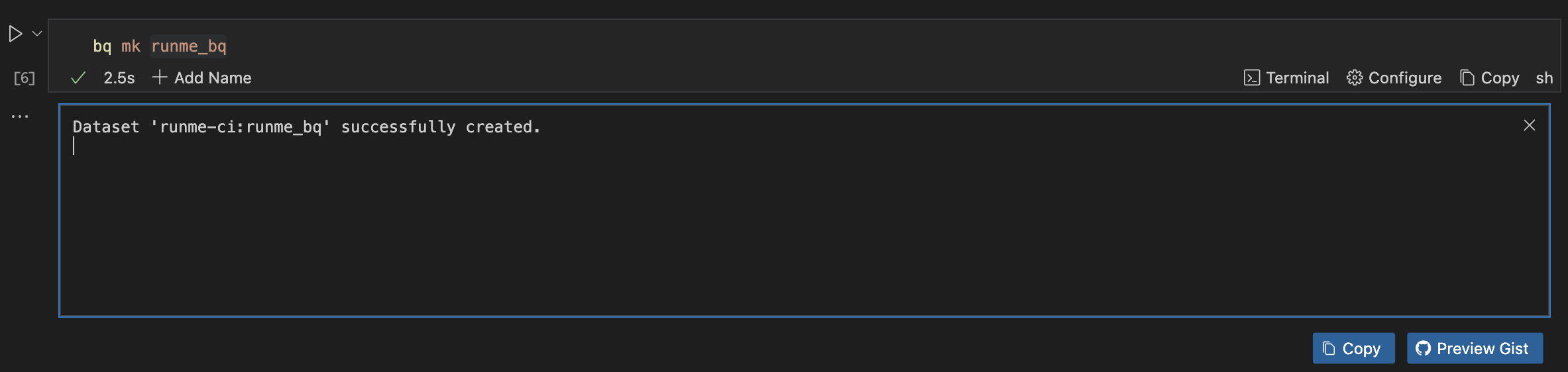
If you need to create a new dataset, run the command below.
bq mk runme_bq
- Delete Dataset
To delete all tables and views within the dataset, run the command below.
bq rm -r -f [PROJECT_ID]:[DATASET]
Replace PROJECT_ID and DATASET with your information, and run the command to delete a dataset.
- Creating a Table
To create a new table within your dataset, run the command below.
bq mk --table [DATASET].[TABLE]
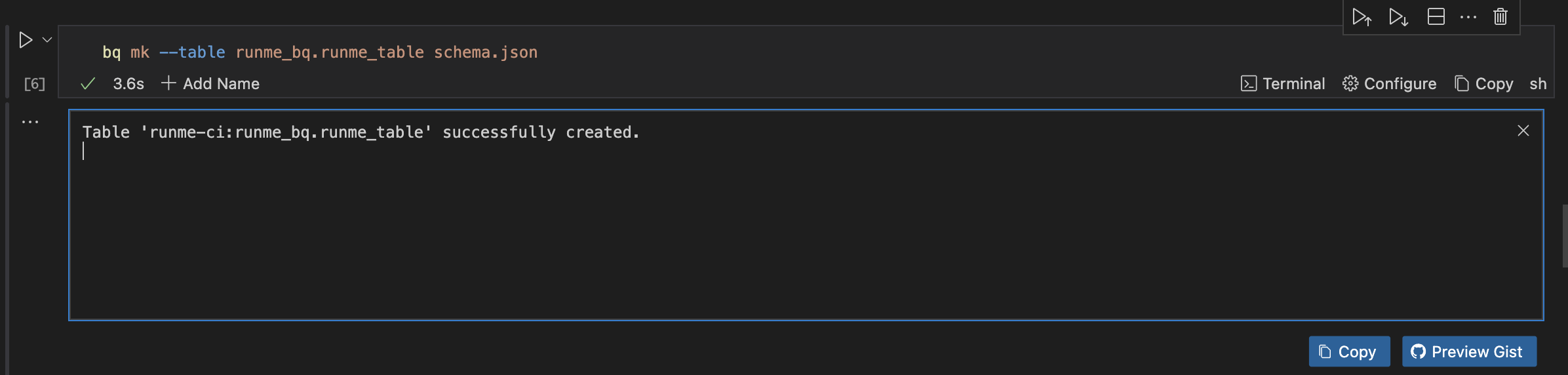
Replace DATASET and TABLE with your information, like the code block below, and run the command to create a table.
bq mk --table [DATASET].[TABLE] schema.json
- Delete a Table
To delete a table from your BigQuery, run the command below
bq rm -f [DATASET].[TABLE]
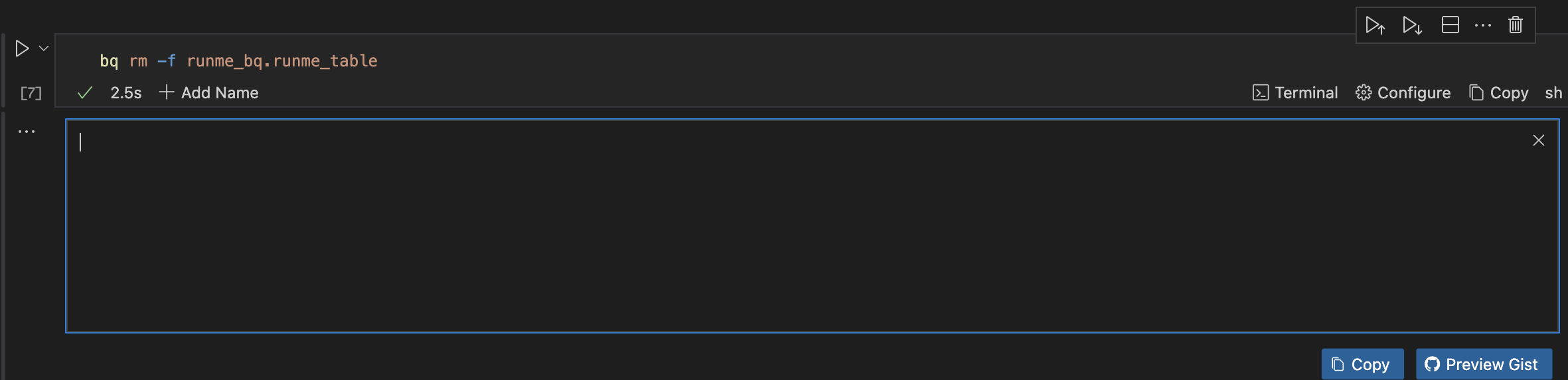
Replace DATASET and TABLE with your information, like the code block below, and run the command to delete a table.
bq rm -f runme_bq.runme_table
This command forcefully deletes the table named runme_table in the dataset runme_bq
- Create a Table with Expiration Time
You can create a partitioned table with expiration in BigQuery. Run the command below to do this.
bq mk --table --time_partitioning_expiration 2592000000 my_dataset.temporary_data schema.json
Getting Help
If you need additional help with BigQuery commands, you can view the help documentation:
bq --help
Feedback
You have successfully set up and configured Google BigQuery and executed SQL queries on BigQuery within your Runme notebook. We are constantly developing more features for Runme. If you have feedback on this or new ideas for improving this feature, feel free to contact us.